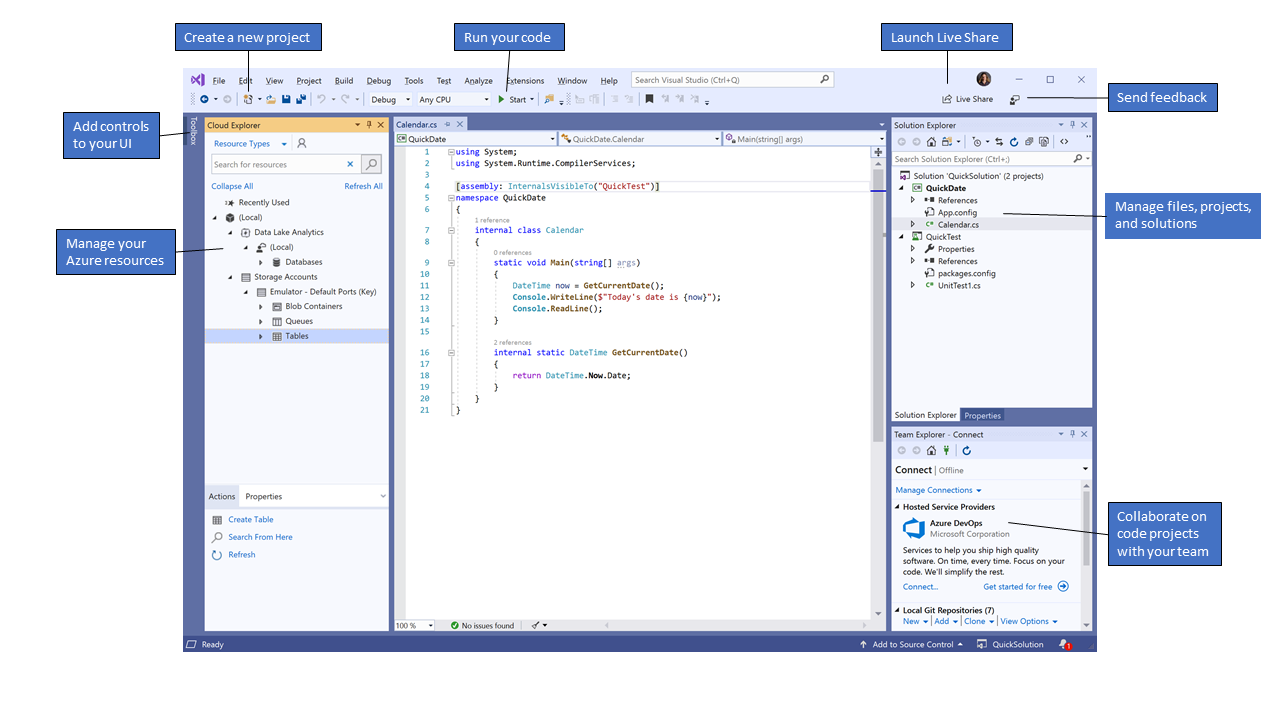
Visual Studio 통합 개발 환경은 코드를 편집, 디버그 및 빌드한 다음, 앱을 게시하는 데 사용할 수 있는 창의적인 실행 패드입니다.IDE(통합 개발 환경)는 소프트웨어 개발의 다양한 측면에서 사용할 수 있는 다양한 기능을 갖춘 프로그램입니다. Visual Studio는 대부분의 IDE가 제공하는 표준 편집기 및 디버거로서 뿐만 아니라, 컴파일러와 코드 완성 도구, 그래픽 디자이너를 비롯해 소프트웨어 개발 프로세스를 쉽게 만들어 주는 많은 기능을 포함하고 있습니다.
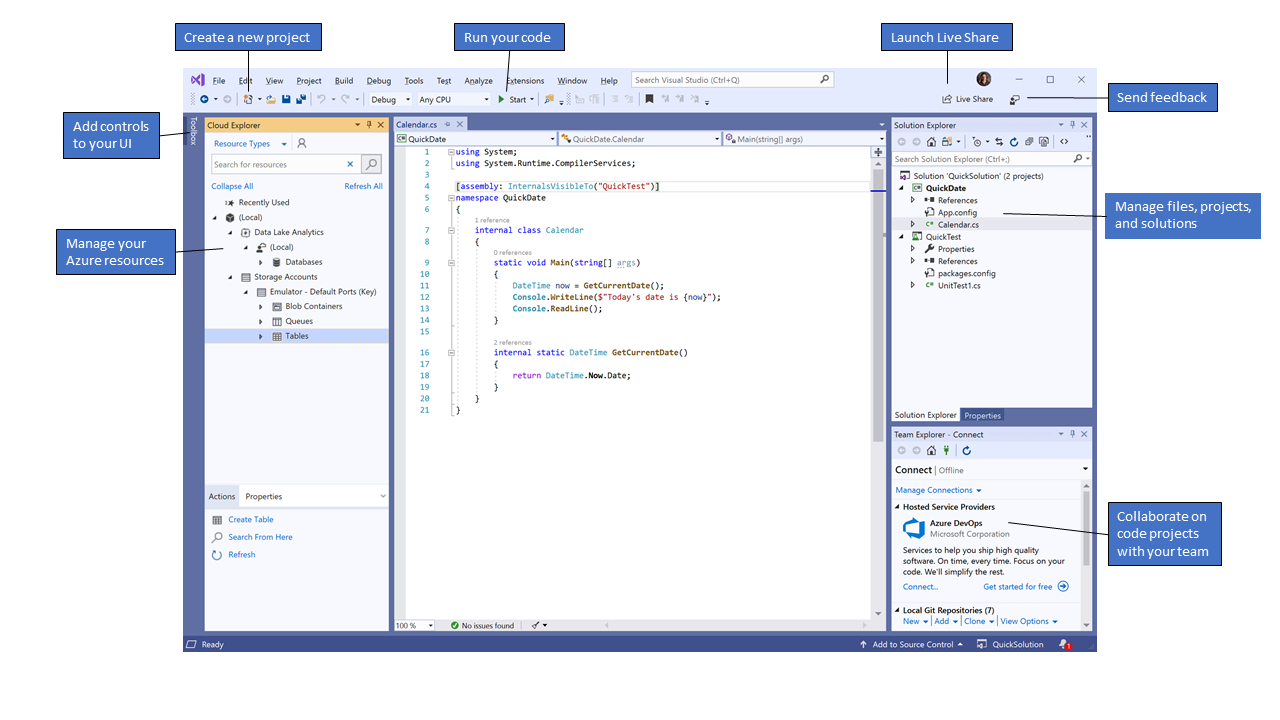
이 이미지는 프로젝트와 사용할 만한 몇 가지 주요 도구 창이 열려 있는 Visual Studio를 보여줍니다.
-
솔루션 탐색기(오른쪽 위) - 코드 파일을 보고, 탐색하고, 관리할 수 있습니다. 솔루션 탐색기에서 파일을 솔루션 및 프로젝트로 그룹화하여 코드를 구성할 수 있습니다.
-
편집기 창(가운데) - 대부분 작업을 수행하는 곳으로 파일 콘텐츠가 표시됩니다. 코드를 편집하거나 단추 및 텍스트 상자를 사용하여 창과 같은 사용자 인터페이스를 디자인할 수 있습니다.
- 팀 탐색기(오른쪽 아래) - Git, TFVC(Team Foundation 버전 제어) 등의 버전 제어 기술을 통해 작업 항목을 추적하고 다른 사용자와 코드를 공유할 수 있습니다.
버전
Visual Studio는 Windows 및 Mac에서 사용할 수 있습니다. Mac용 Visual Studio에는 Visual Studio 2019와 동일한 기능이 많이 있으며 플랫폼 간 앱 및 모바일 앱 개발에 최적화되어 있습니다. 이 문서에서는 Windows 버전의 Visual Studio 2019에 중점을 둡니다.
세 가지 Visual Studio 2019 버전은 다음과 같습니다. Community, Professional 및 Enterprise. 각 버전에서 지원되는 기능에 대해 알아보려면 Visual Studio IDE 비교를 참조하세요.
주요 생산성 향상 기능
소프트웨어를 개발할 때 생산성을 높이는 데 도움이 되는 Visual Studio에서 인기 있는 기능 몇 가지는 다음과 같습니다.
-
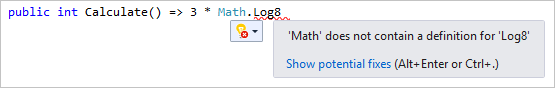
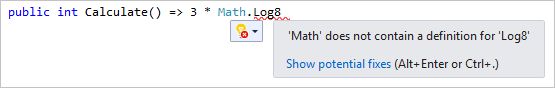
오류 표시선 및 빠른 작업
오류 표시선은 물결 모양의 밑줄로, 입력할 때 코드의 오류 또는 잠재적인 문제를 알려줍니다. 이러한 시각적 단서를 사용하면 빌드하는 동안이나 프로그램을 실행할 때 오류가 검색될 때까지 기다리지 않고 즉시 문제를 해결할 수 있습니다. 오류 표시선 위로 마우스를 가져가면 오류에 대한 추가 정보가 표시됩니다. 오류를 수정하기 위한 작업(빠른 작업이라고 함)과 함께 전구가 왼쪽 여백에 나타날 수도 있습니다.
-
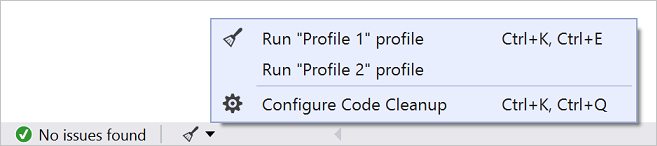
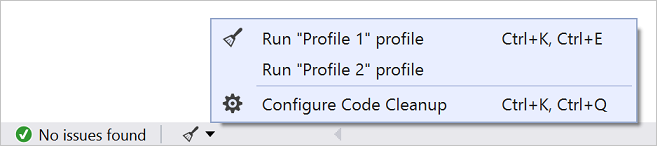
코드 정리
단추를 클릭하여 코드 형식을 지정하고 코드 스타일 설정, .editorconfig 규칙 및 Roslyn 분석기에서 제안하는 코드 수정 사항을 적용합니다. 코드 정리는 코드 검토로 이동하기 전에 코드의 문제를 해결하는 데 도움이 됩니다. (현재 C# 코드에만 사용할 수 있습니다.)
-
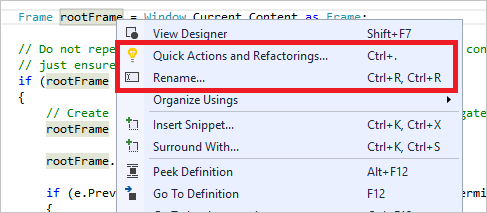
리팩터링에는 변수의 지능형 이름 바꾸기, 새 메서드로 코드 줄을 하나 이상 추출, 메서드 매개 변수의 순서 변경 등과 같은 작업이 포함됩니다.
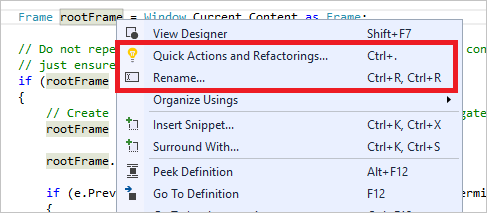
-
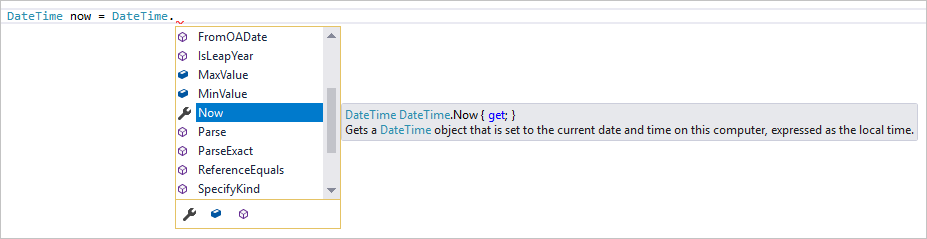
IntelliSense는 편집기에서 직접 코드에 대한 정보를 표시하고 경우에 따라 약간의 코드를 작성하는 기능 집합에 대한 용어입니다.IntelliSense는 다른 곳에서 형식 정보를 조회할 필요가 없도록 기본 설명서를 편집기에 인라인으로 포함하는 것과 같습니다.IntelliSense 기능은 언어에 따라 달라집니다. 자세한 내용은 C# IntelliSense, Visual C++ IntelliSense, JavaScript IntelliSense 및 Visual Basic IntelliSense를 참조하세요. 다음 그림에서는 IntelliSense에서 형식에 대한 멤버 목록을 표시하는 방법을 보여 줍니다.
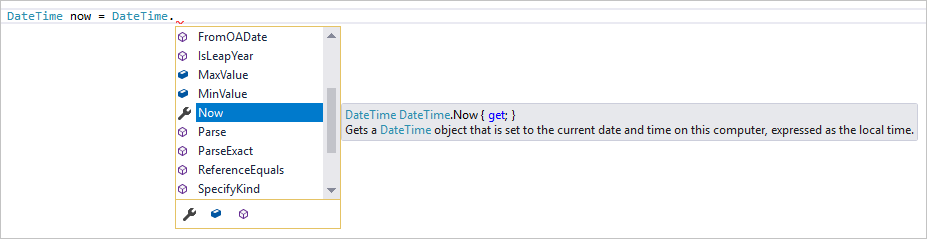
-
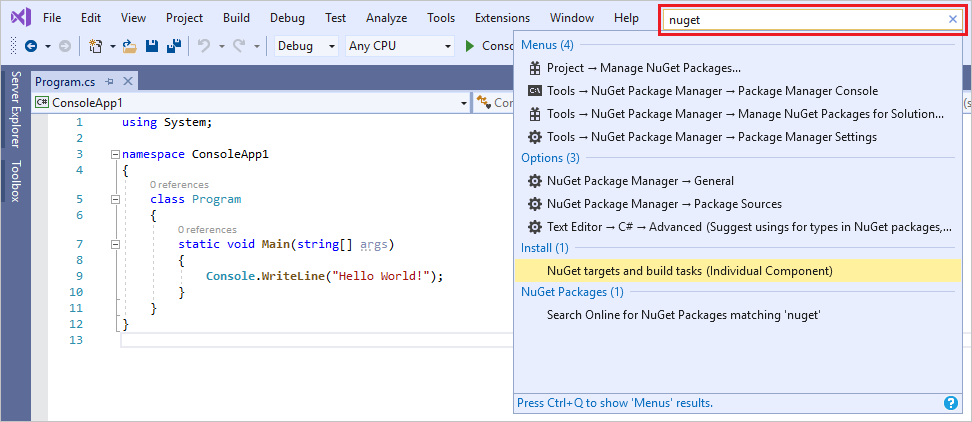
검색 상자
Visual Studio는 메뉴, 옵션 및 속성이 매우 다양하여 때때로 버거울 수도 있습니다. 검색 상자는 Visual Studio에서 필요한 항목을 빠르게 찾을 수 있는 좋은 방법입니다. 찾으려는 이름을 입력하기만 하면 Visual Studio는 원하는 곳으로 정확하게 안내하는 결과를 나열합니다. 예를 들어 다른 프로그래밍 언어를 위한 지원을 추가하도록 Visual Studio에 기능을 추가하는 경우 검색 상자를 사용하면 워크로드 또는 개별 구성 요소를 설치하도록 Visual Studio 설치 관리자가 열립니다.
팁
검색 상자에 대한 바로 가기는 Ctrl+Q를 누릅니다.
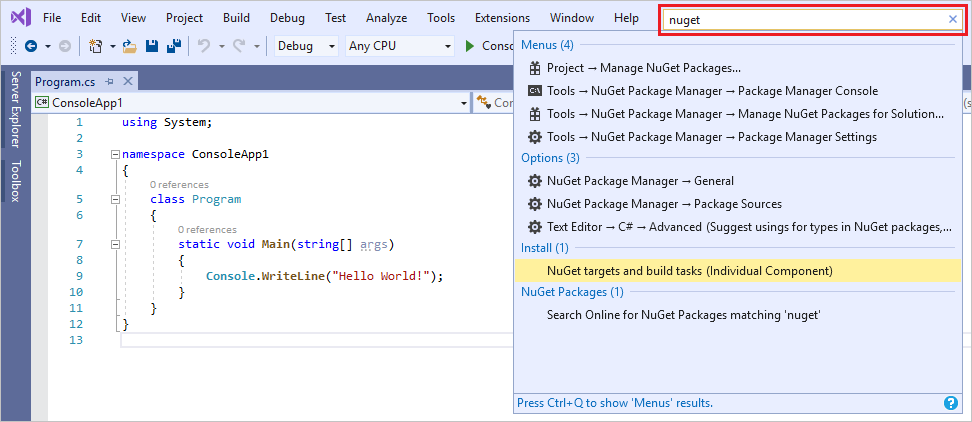
-
앱 유형 또는 프로그래밍 언어와 관계없이 다른 사람과 공동으로 실시간 편집 및 디버그를 수행할 수 있습니다. 프로젝트를 즉시 안전하게 공유하고, 필요에 따라 디버깅 세션, 터미널 인스턴스, localhost 웹앱, 음성 통화 등을 공유할 수 있습니다.
-
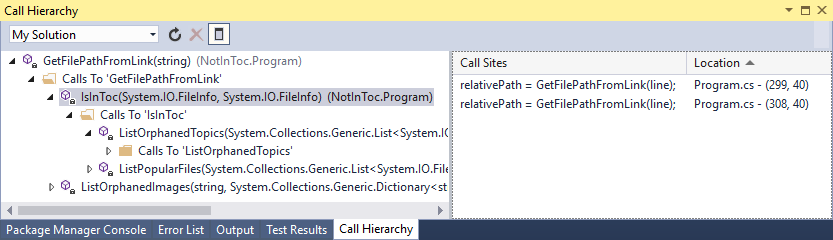
호출 계층 구조 창은 선택한 메서드를 호출하는 방법을 보여 줍니다. 이는 메서드를 변경하거나 제거하려고 하거나 버그를 추적하려는 경우 유용한 정보가 됩니다.
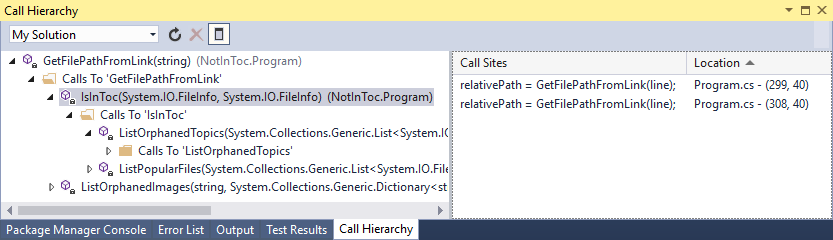
-
CodeLens를 사용하면 편집기 내에서 코드 참조, 코드 변경 내용, 연결된 버그, 작업 항목, 코드 검토 및 단위 테스트를 확인할 수 있습니다.
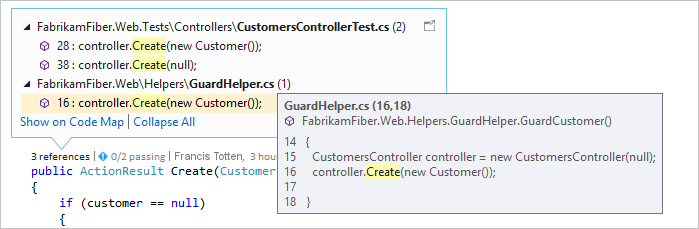
-
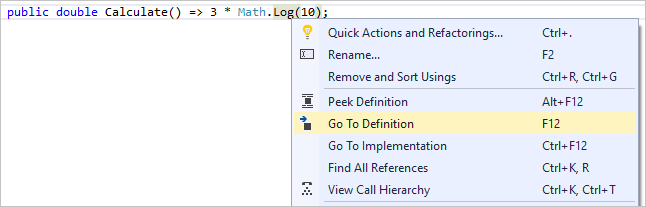
정의로 이동 기능은 함수 또는 형식이 정의된 위치로 직접 이동합니다.
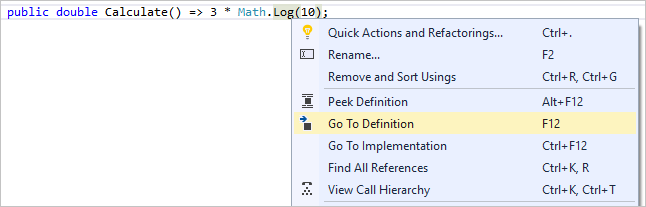
-
정의 보기 창은 실제로 개별 파일을 열지 않고 메서드 또는 형식의 정의 보여 줍니다.
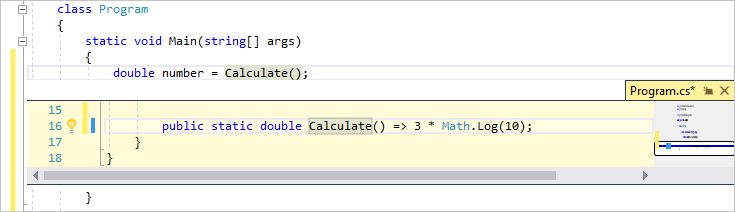
Visual Studio IDE 설치
이 섹션에서는 Visual Studio로 할 수 있는 몇 가지 작업을 시도해 볼 간단한 프로젝트를 만듭니다. 코딩 지원 기능인 IntelliSense를 사용하고, 앱을 디버그하여 프로그램을 실행하는 동안 변수 값이 표시되도록 하고, 색 테마를 변경합니다.
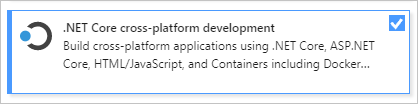
시작하려면 Visual Studio를 다운로드하여 시스템에 설치합니다. 모듈식 설치 관리자를 사용하면 선호하는 프로그래밍 언어 또는 플랫폼에 필요한 기능 그룹인 워크로드를 선택하여 설치할 수 있습니다. 프로그램 생성 단계를 수행하려면 설치 중에 .NET Core 플랫폼 간 개발 워크로드를 선택해야 합니다.
Visual Studio를 처음 열면 필요에 따라 Microsoft 계정이나 회사 또는 학교 계정으로 로그인할 수 있습니다.
프로그램 만들기
이제 본격적으로 간단한 프로그램을 만들어 보겠습니다.
-
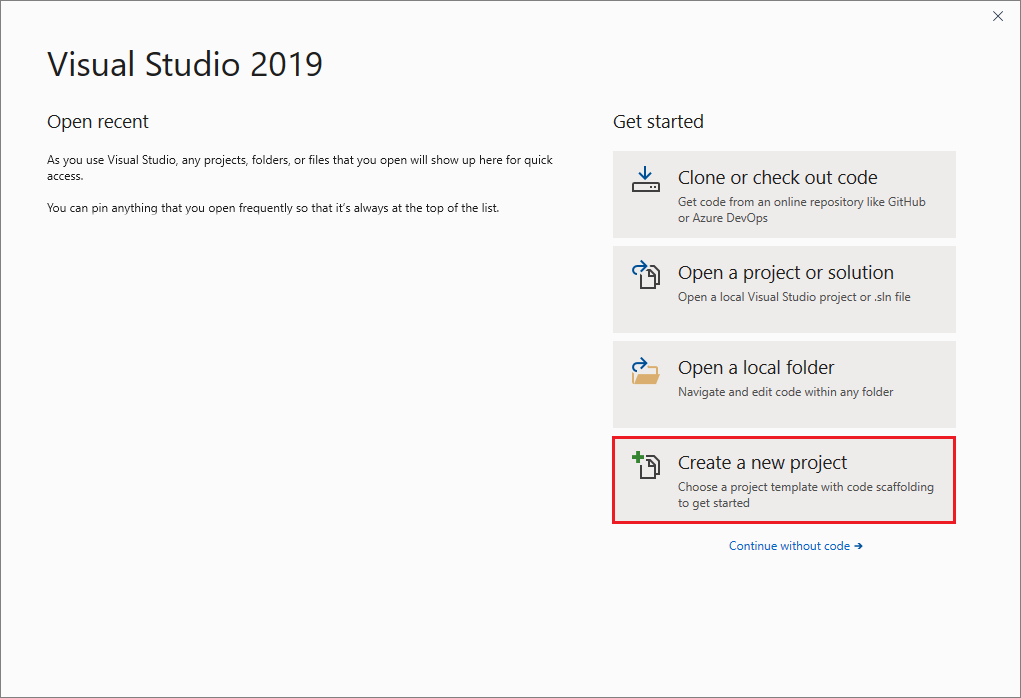
Visual Studio를 엽니다.
리포지토리 복제, 최근 프로젝트 열기 또는 새 프로젝트 만들기에 대한 다양한 옵션이 포함되어 있는 시작 창이 표시됩니다.
-
새 프로젝트 만들기를 선택합니다.
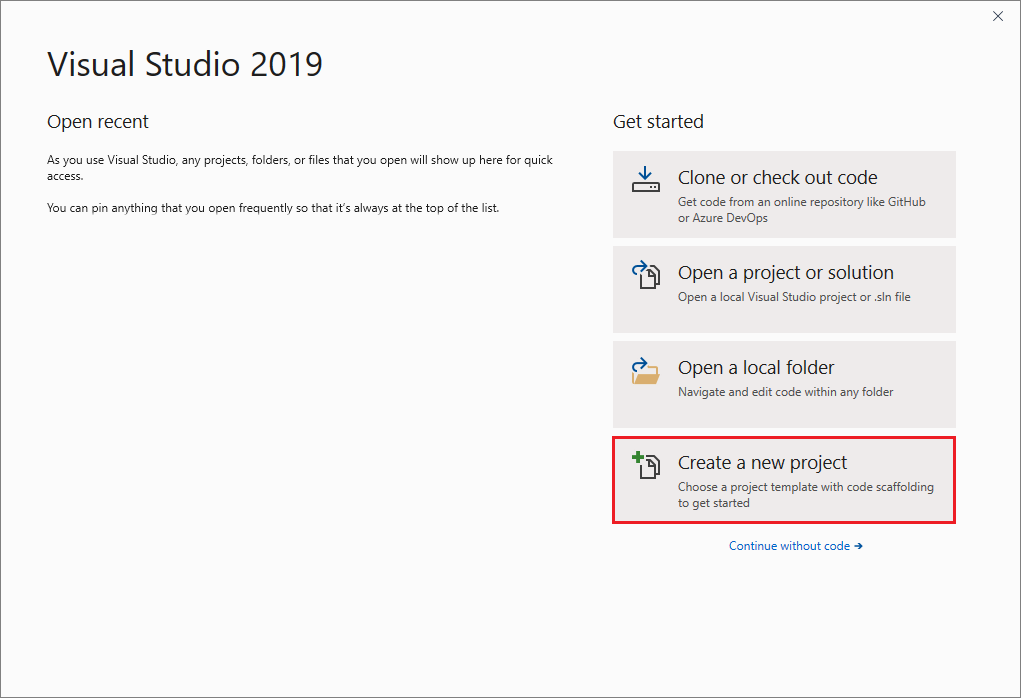
새 프로젝트 만들기 창이 열리고 여러 프로젝트 템플릿이 표시됩니다. 템플릿에는 지정된 프로젝트 형식에 필요한 기본 파일과 설정이 포함되어 있습니다.
-
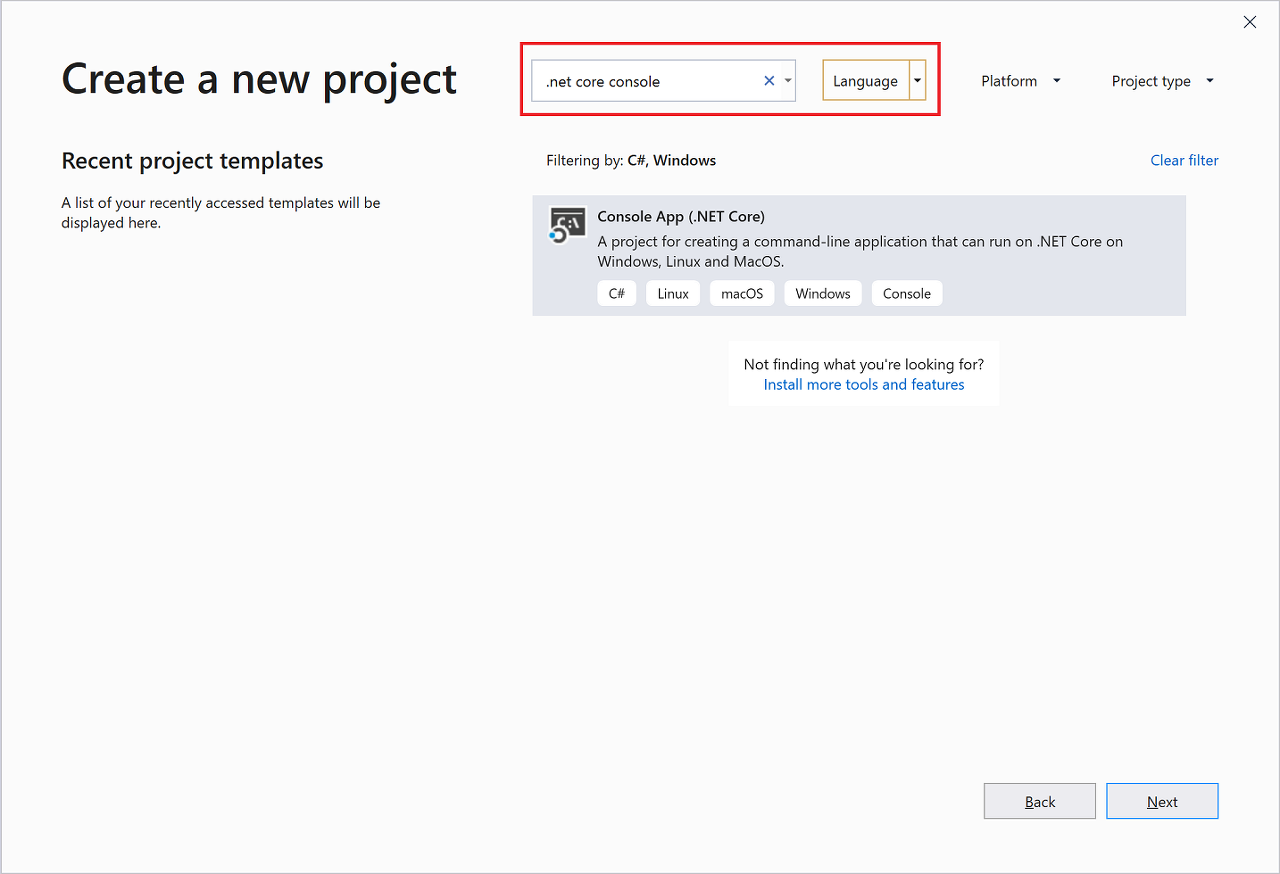
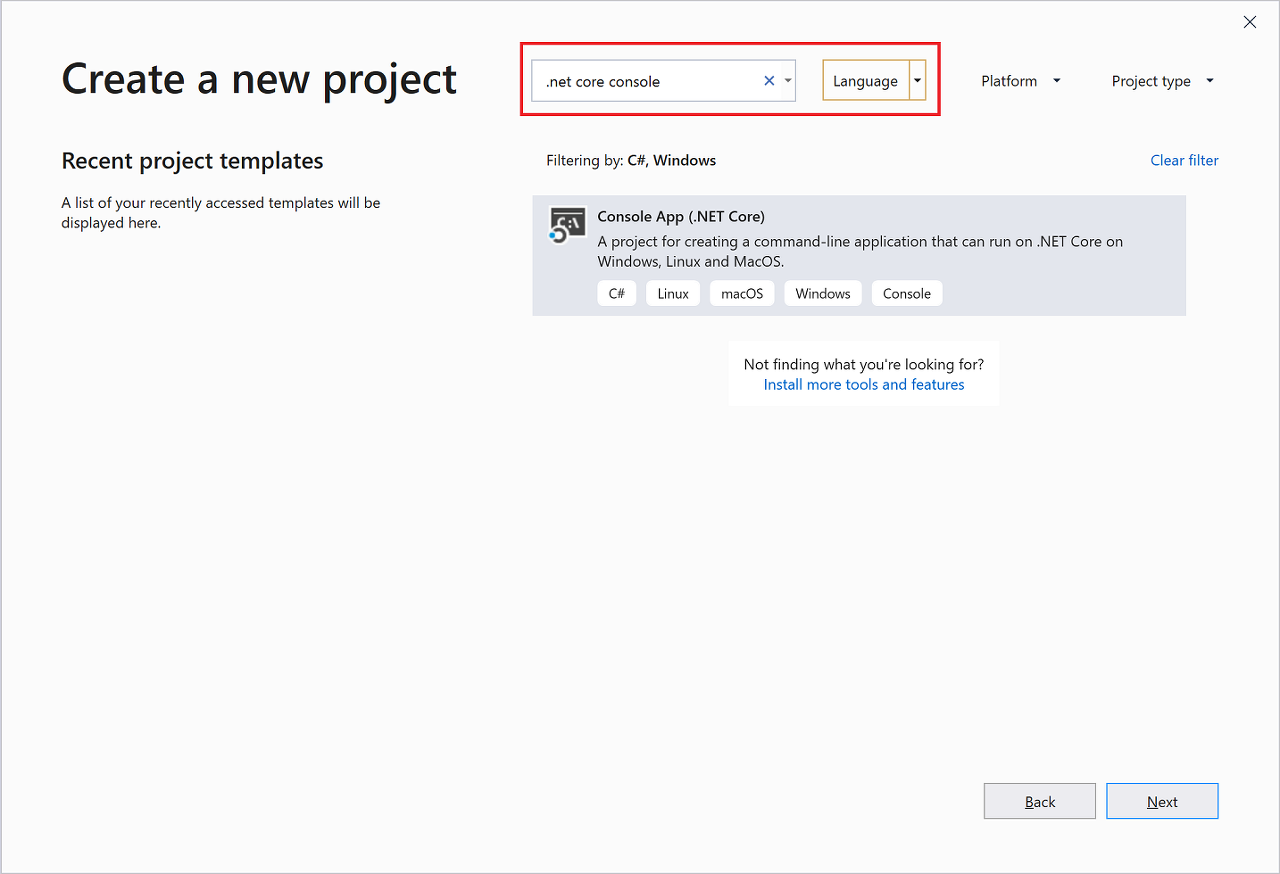
원하는 템플릿을 찾으려면 검색 상자에 .net core console을 입력합니다. 입력한 키워드에 따라 사용 가능한 템플릿 목록이 자동으로 필터링됩니다. 언어 드롭다운 목록에서 C# 를 선택하여 추가로 템플릿 결과를 필터링할 수 있습니다. 콘솔 앱(.NET Core) 템플릿을 선택하고 다음을 선택합니다.
-
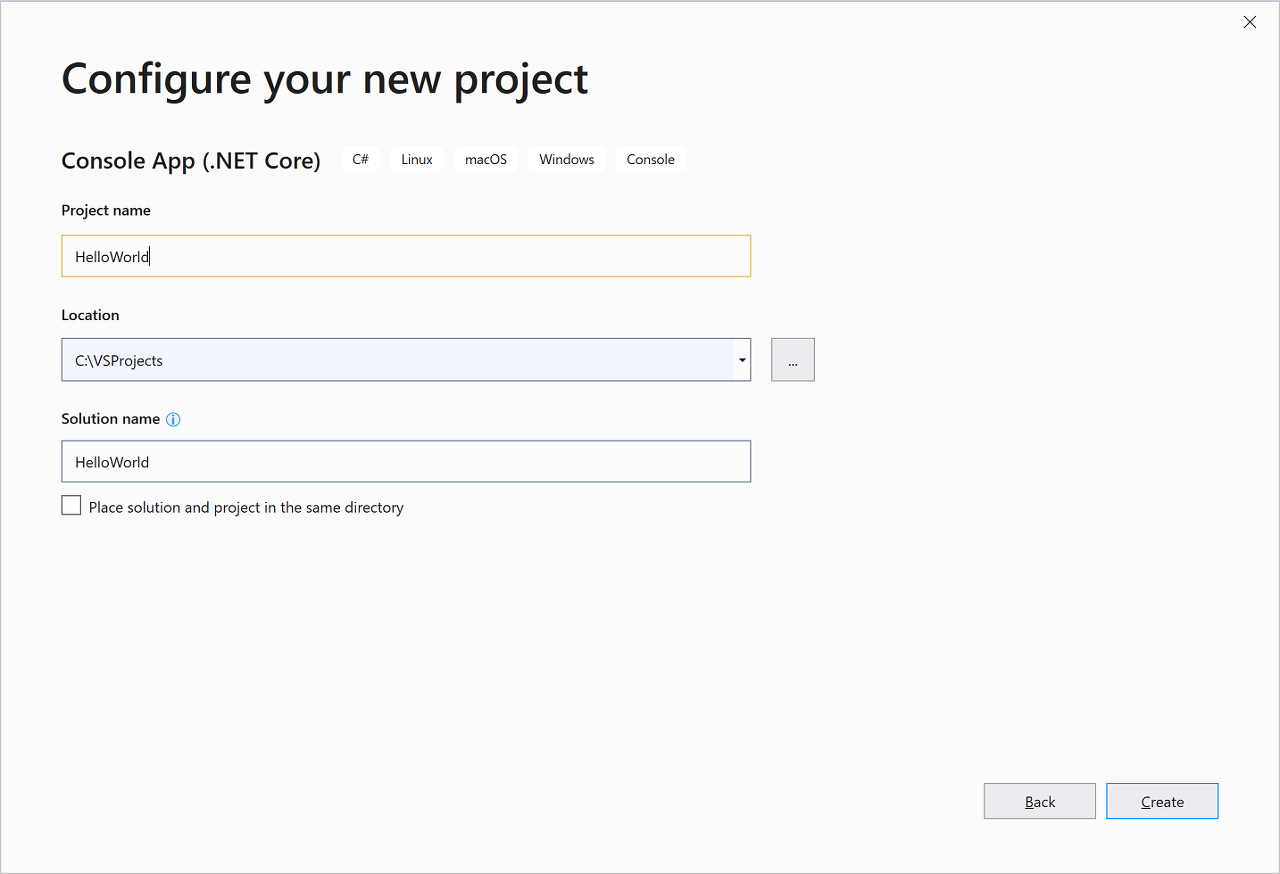
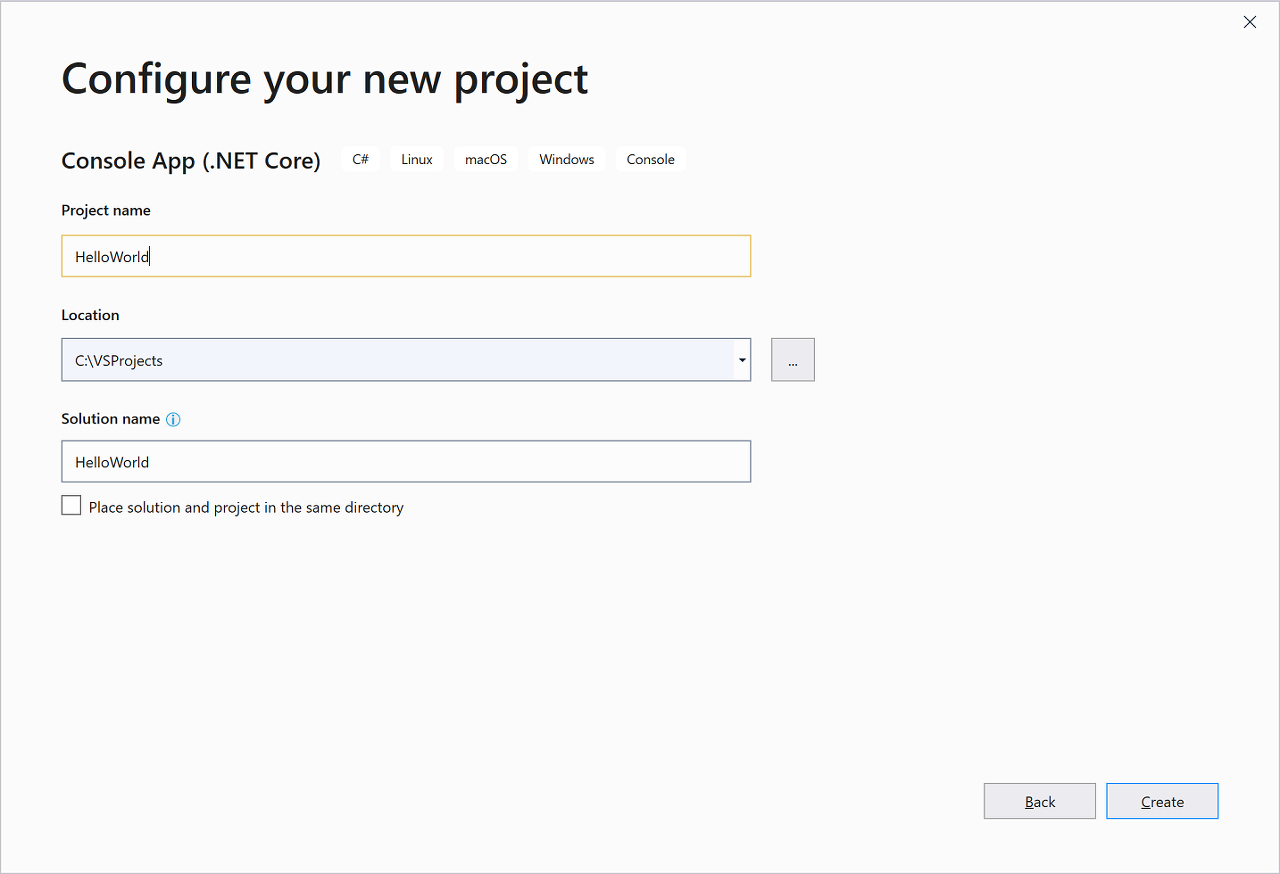
새 프로젝트 구성 창에서 프로젝트 이름 상자에 HelloWorld를 입력하고, 필요에 따라 프로젝트 파일의 디렉터리 위치를 변경한 다음, 만들기를 선택합니다.
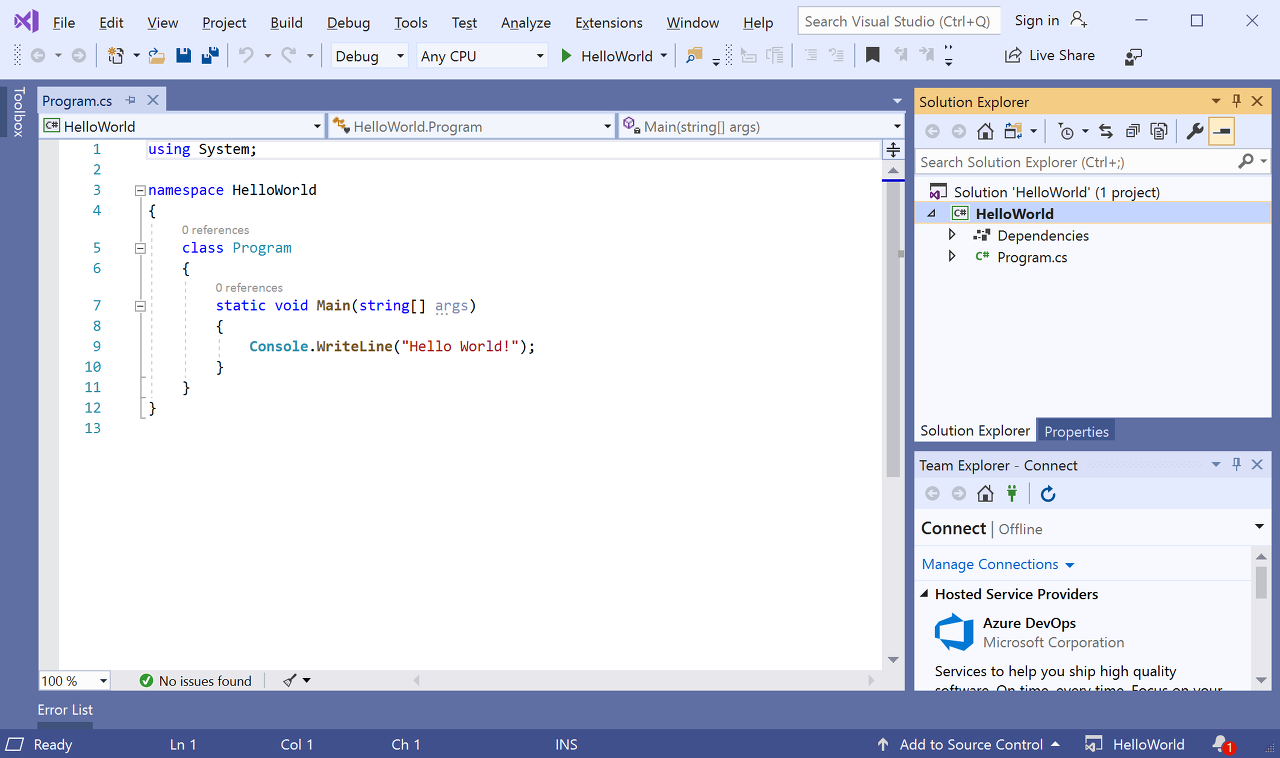
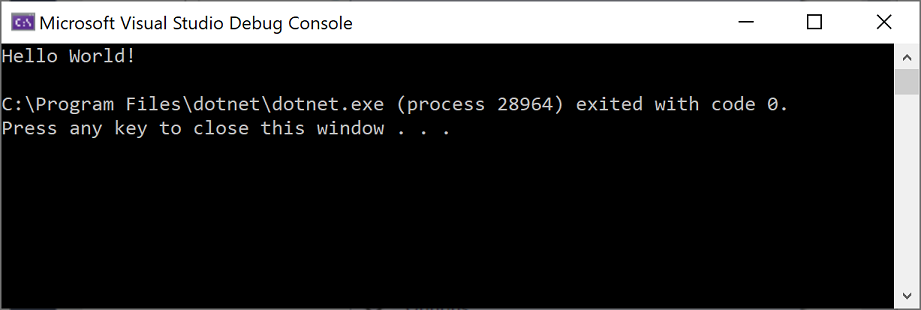
Visual Studio가 프로젝트를 만듭니다. 이 프로젝트는 Console.WriteLine() 메서드를 호출하여 리터럴 문자열 “Hello World!”를 표시하는 간단한 “Hello World” 애플리케이션입니다. 콘솔(프로그램 출력) 창에서
잠시 후 다음과 같은 정보가 표시됩니다.
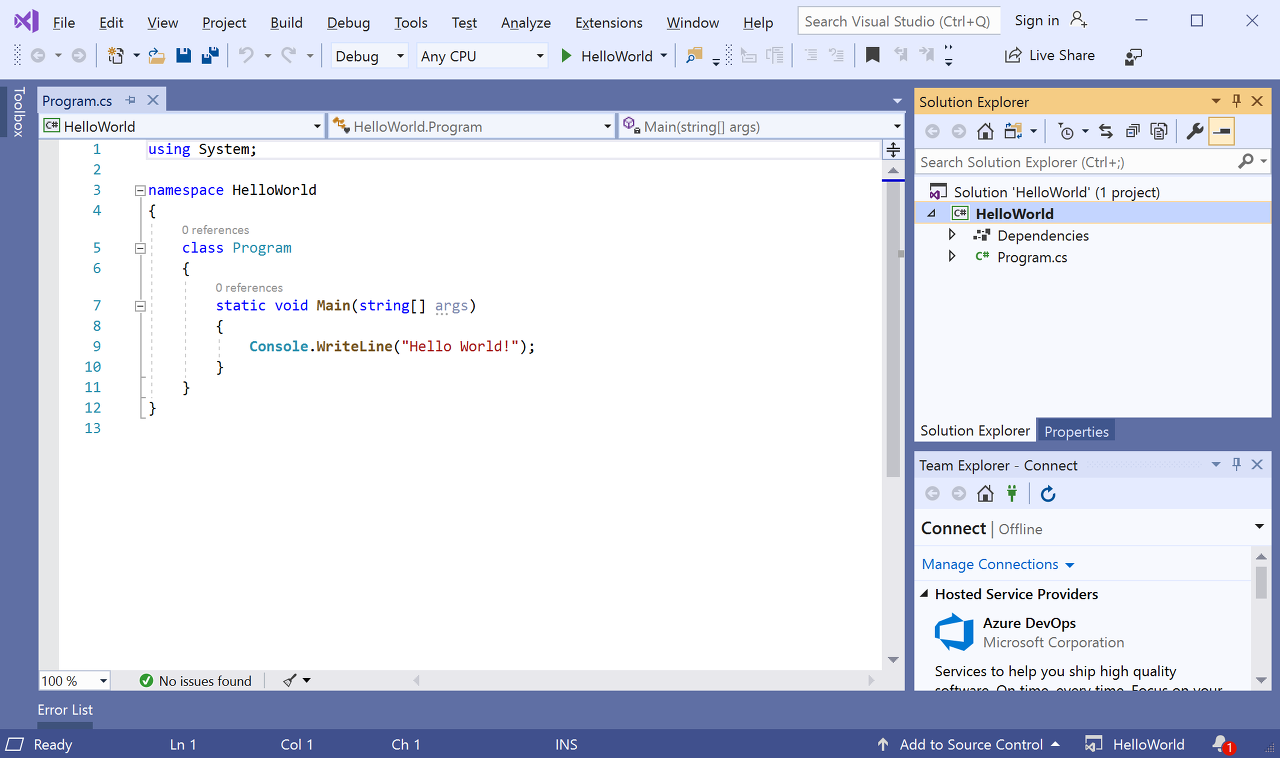
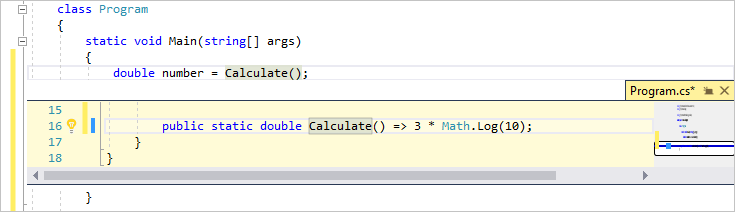
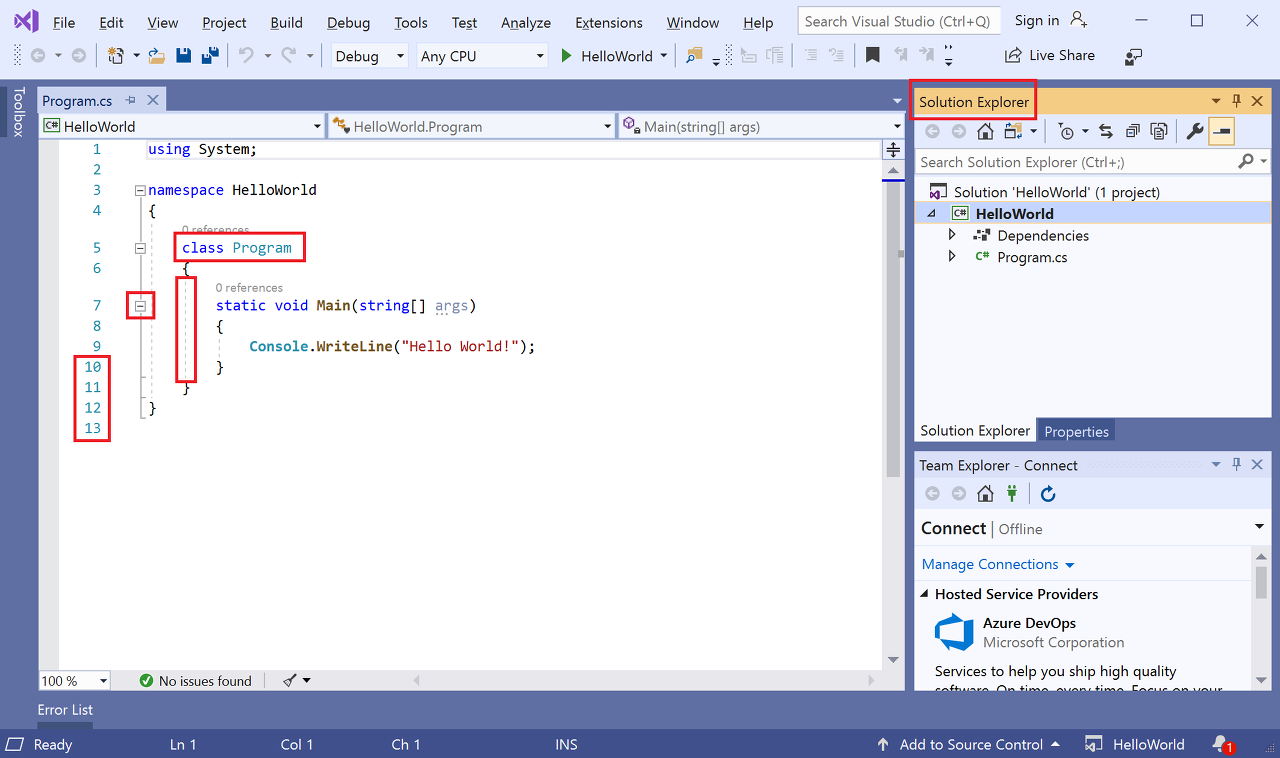
애플리케이션의 C# 코드는 대부분의 공간을 차지하는 편집기 창에 표시됩니다. 텍스트는 지정된 색으로 자동으로 표시되어 다른 부분(예: 키워드 또는 형식)을 나타냅니다. 또한 코드에서 작은 세로 파선은 서로 일치하는 중괄호를 나타내며, 줄 번호는 나중에 코드를 찾는 데 도움이 됩니다. 작은 상자 안에 있는 빼기 기호를 선택하여 코드 블록을 축소하거나 확장할 수 있습니다. 이 코드 개요 기능을 사용하면 필요 없는 코드를 숨길 수 있으므로 화면 상의 혼란을 최소화할 수 있습니다. 프로젝트 파일은 솔루션 탐색기라는 창의 오른쪽에 나열됩니다.
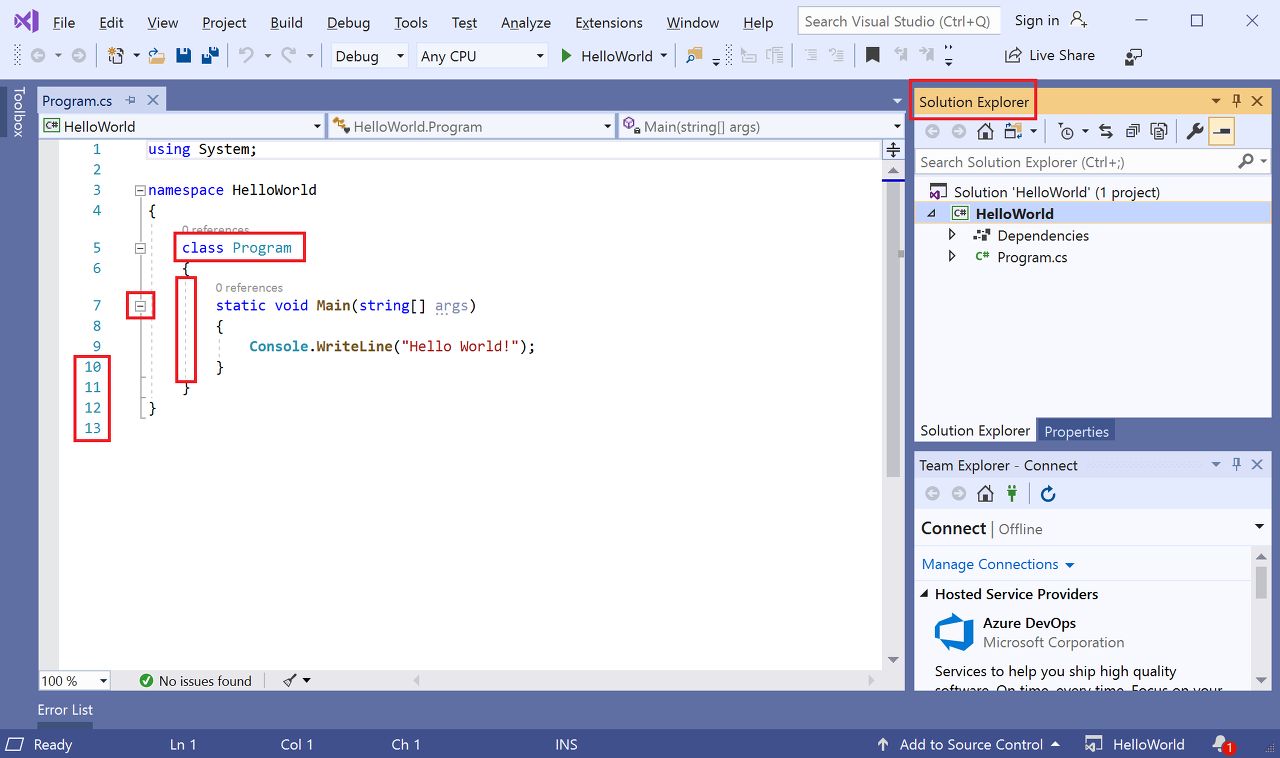
다른 메뉴와 도구 창을 사용할 수 있지만 지금은 넘어가겠습니다.
-
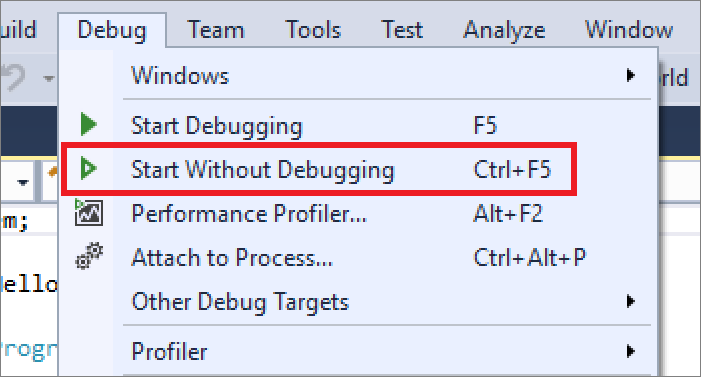
이제 앱을 시작합니다. 메뉴 모음의 디버그 메뉴에서 디버깅하지 않고 시작을 선택하면 됩니다. Ctrl+F5를 누를 수도 있습니다.
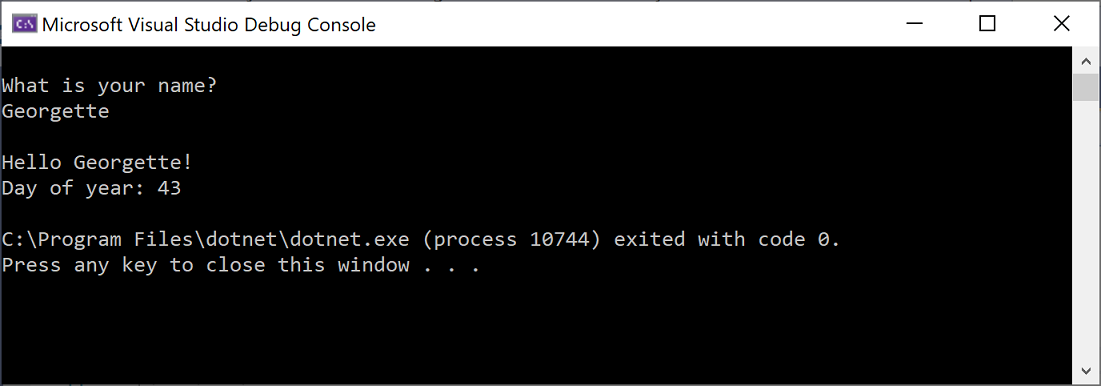
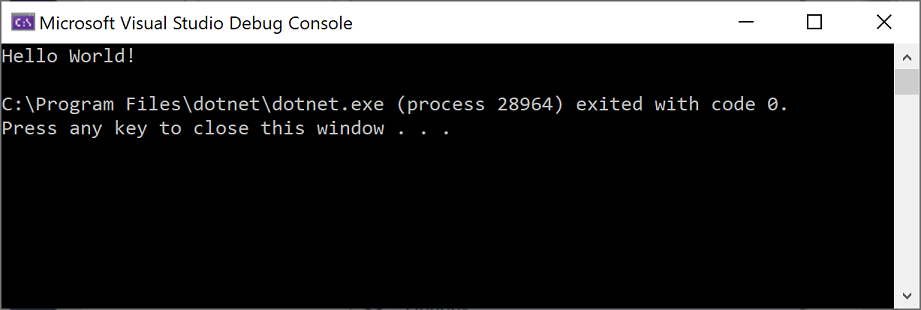
Visual Studio에서 앱을 빌드하며, 콘솔 창이 열리고 Hello World! 메시지가 표시됩니다. 이제 실행 중인 앱이 있습니다!
-
콘솔 창을 닫으려면 키보드에서 아무 키나 누릅니다.
-
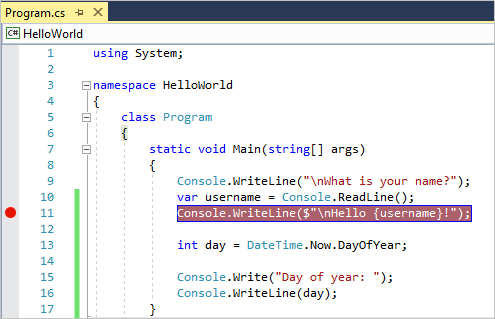
앱에 일부 코드를 추가하겠습니다. Console.WriteLine("Hello World!"); 줄 앞에 다음 C# 코드를 추가합니다.
C#복사
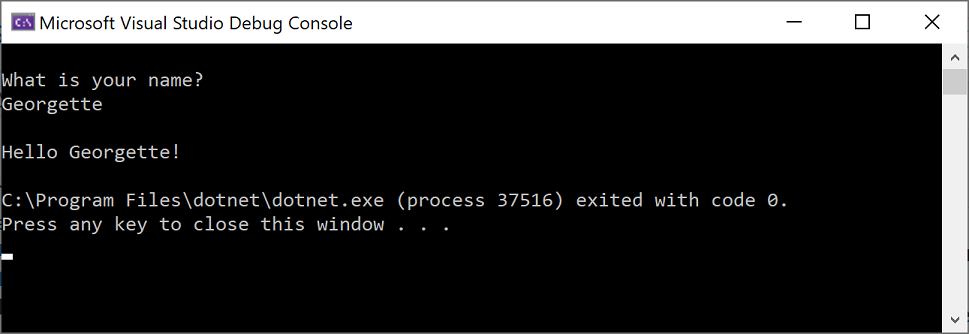
Console.WriteLine("\nWhat is your name?"); var name = Console.ReadLine();이 코드는 콘솔 창에 이름이 무엇입니까? 를 표시한 다음, 사용자가 텍스트를 입력한 후 Enter 키를 누를 때까지 기다립니다.
-
Console.WriteLine("Hello World!");이라고 표시된 줄을 다음 코드로 변경합니다.
C#복사
Console.WriteLine($"\nHello {name}!"); -
디버그 > 디버깅 없이 시작을 선택하거나 Ctrl+F5를 눌러 앱을 다시 실행합니다.
Visual Studio에서 앱을 다시 빌드하고, 콘솔 창이 열리며 사용자 이름을 묻는 메시지가 표시됩니다.
-
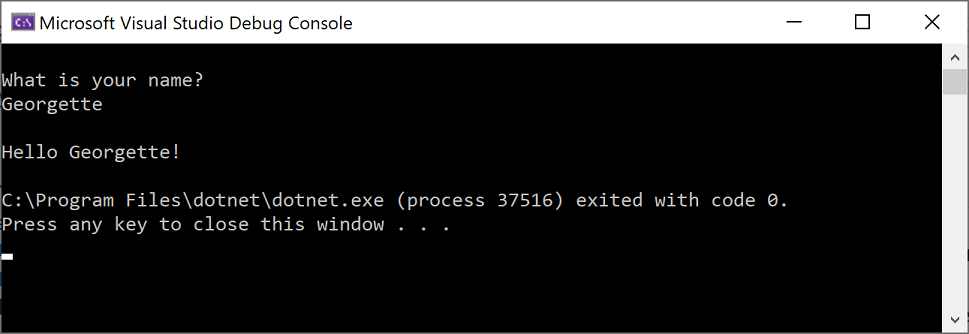
콘솔 창에 이름을 입력하고 Enter 키를 누릅니다.
-
아무 키나 눌러 콘솔 창을 닫고 실행 중인 프로그램을 중지합니다.
리팩터링 및 IntelliSense 사용
리팩터링 및 IntelliSense로 더 효율적으로 코딩하는 데 도움이 되는 몇 가지 방법을 살펴보겠습니다.
먼저 name 변수의 이름을 변경합니다.
-
name 변수를 두 번 클릭하여 선택합니다.
-
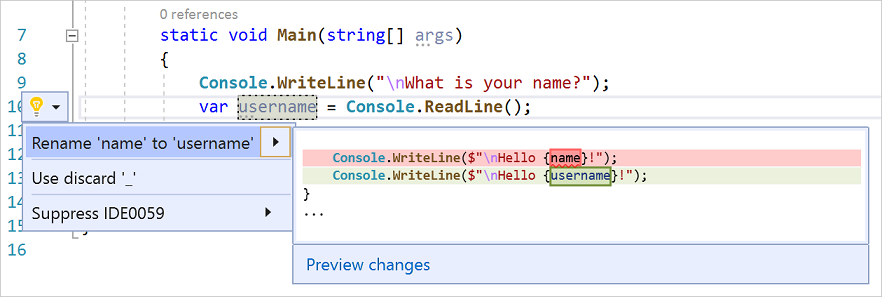
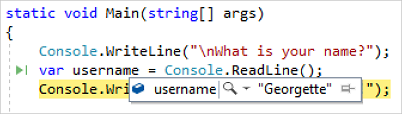
변수의 새 이름 username을 입력합니다.
변수 주위에 회색 상자가 나타나고 여백에 전구가 나타납니다.
-
전구 아이콘을 선택하여 사용 가능한 빠른 작업을 표시합니다. 'name'의 이름을 'username'으로 바꾸기를 선택합니다.
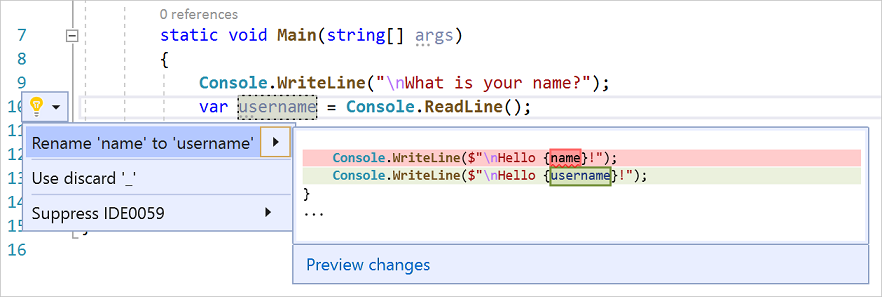
프로젝트 전체에서 변수의 이름이 변경됩니다. 이 경우에는 두 군데밖에 없습니다.
-
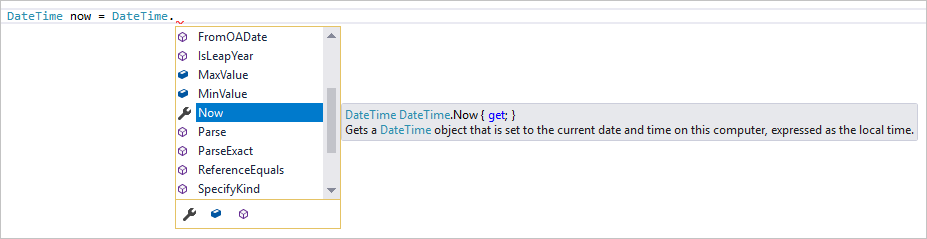
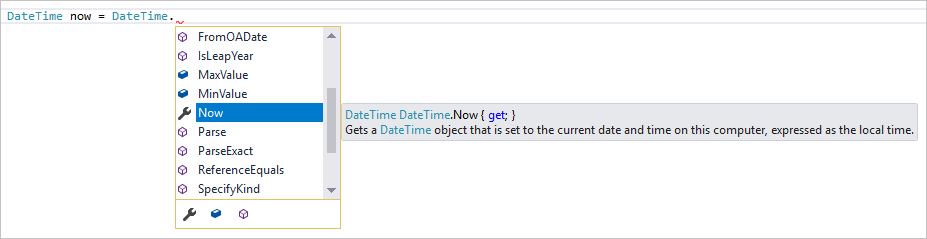
이제 IntelliSense를 살펴보겠습니다. Console.WriteLine($"\nHello {username}!");이라고 표시된 줄 아래에 DateTime now = DateTime.을 입력합니다.
상자에 DateTime 클래스의 멤버가 표시됩니다. 또한 현재 선택된 멤버의 설명이 별도 상자에 표시됩니다.
-
클래스의 속성인 Now라는 멤버를 두 번 클릭하거나 Tab 키를 눌러 선택합니다. 끝에 세미콜론을 추가하여 코드 줄을 완성합니다.
-
그 아래에 다음 코드 줄을 입력하거나 붙여넣습니다.
C#복사
int dayOfYear = now.DayOfYear; Console.Write("Day of year: "); Console.WriteLine(dayOfYear);팁
Console.Write은 인쇄 후 줄 종결자를 추가하지 않는다는 점에서 Console.WriteLine과 약간 다릅니다. 즉, 출력으로 전송되는 다음 텍스트가 같은 줄에 인쇄됩니다. 코드에서 이러한 각 메서드 위로 마우스를 가져가면 설명을 볼 수 있습니다.
-
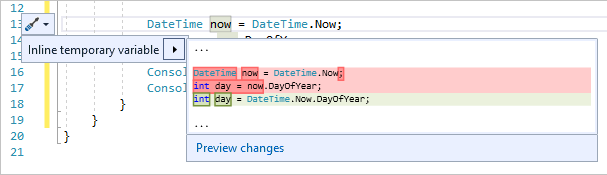
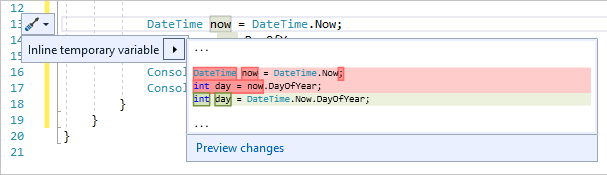
다음으로, 리팩터링을 다시 사용하여 코드를 좀 더 간결하게 만듭니다. DateTime now = DateTime.Now; 줄에서 변수 now를 클릭합니다.
해당 줄의 여백에 작은 스크루드라이버 아이콘이 나타납니다.
-
스크루드라이버 아이콘을 클릭하면 Visual Studio에서 제안하는 사항을 볼 수 있습니다. 여기에는 코드의 전체 동작을 변경하지 않고 코드 줄을 제거할 수 있는 인라인 임시 변수 리팩터링이 표시되어 있습니다.
-
인라인 임시 변수를 클릭하여 코드를 리팩터링합니다.
-
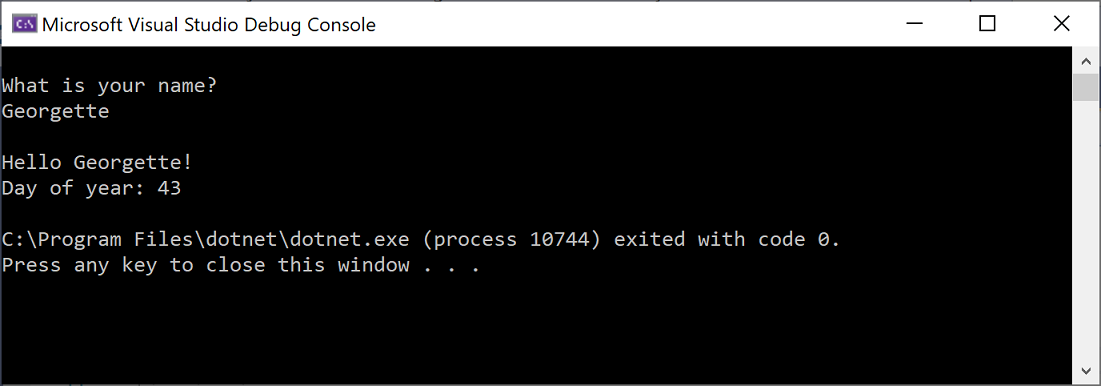
Ctrl+F5 키를 눌러 프로그램을 다시 실행합니다. 출력은 다음과 같습니다.
코드 디버그
코드를 작성할 때 코드를 실행하고 버그를 테스트해야 합니다. Visual Studio의 디버깅 시스템을 사용하면 코드를 단계별로 진행하면서 명령문을 한 번에 하나씩 실행하면서 변수를 검사할 수 있습니다. 특정 줄에서 코드의 실행을 중지하는 중단점을 설정할 수 있습니다.코드를 실행함에 따라 변수의 값이 변경되는 방법 등을 확인할 수 있습니다.
중단점을 설정하여 프로그램이 "이동 중"일 때 username 변수의 값을 확인하겠습니다.
-
Console.WriteLine($"\nHello {username}!");이라고 표시된 코드 줄을 찾습니다. 이 코드 줄에 중단점을 설정하려면, 즉 이 줄에서 프로그램이 실행을 일시 중지하도록 하려면 편집기의 맨 왼쪽 여백을 클릭합니다. 코드 줄의 아무 곳이나 클릭한 다음, F9 키를 누를 수도 있습니다.
맨 왼쪽 끝에 빨간색 원이 표시되고 코드가 빨간색으로 강조 표시됩니다.
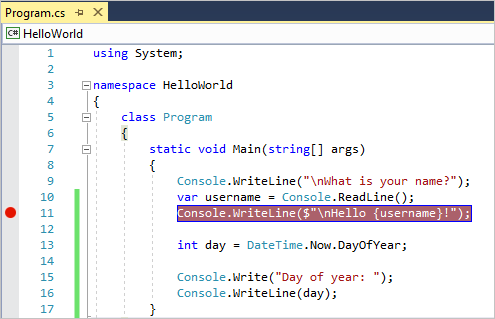
-
디버그 > 디버깅 시작을 선택하거나 F5 키를 눌러 디버깅을 시작합니다.
-
콘솔 창이 나타나고 사용자 이름을 묻는 메시지가 표시되면 입력하고 Enter 키를 누릅니다.
Visual Studio 코드 편집기로 포커스가 돌아오고 중단점이 있는 코드 줄이 노란색으로 강조 표시됩니다. 이는 프로그램이 실행할 다음 코드 줄을 의미합니다.
-
마우스를 username 변수 위로 가져가면 해당 값을 볼 수 있습니다. 또는 username을 마우스 오른쪽 단추로 클릭하고 조사식 추가를 선택하여 변수를 조사식 창에 추가할 수 있습니다. 이 창에서 해당 값을 볼 수도 있습니다.
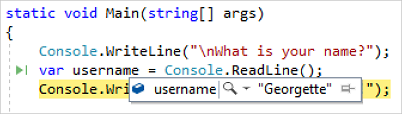
-
프로그램 실행을 완료하려면 F5 키를 다시 누릅니다.
Visual Studio의 디버깅에 대한 자세한 내용은 디버거 기능 둘러보기를 참조하세요.
Visual Studio 사용자 지정
기본 색 테마 변경을 비롯하여 Visual Studio 사용자 인터페이스를 꾸밀 수 있습니다. 어둡게 테마로 변경하려면:
- 메뉴 모음에서 도구 > 옵션을 선택하여 옵션 대화 상자를 엽니다.
-
환경 > 일반 옵션 페이지에서 색 테마 선택을 어둡게로 변경하고 확인을 선택합니다.
전체 IDE의 색 테마가 어둡게로 변경됩니다.
IDE를 개인 설정할 수 있는 다른 방법을 배우려면 Visual Studio 개인 설정을 참조하세요.
다음 단계
이러한 소개 아티클 중 하나와 함께 다음을 수행하여 Visual Studio를 추가로 탐색합니다.
-
코드 편집기를 사용하는 방법 알아보기에서 코드 편집기에 익숙해집니다.
-
프로젝트 및 솔루션에 대해 알아보기에서 Visual Studio가 코드를 구성하는 방법에 대해 알아봅니다.
자세한 코딩을 살펴보려는 경우 다음과 같은 언어별 빠른 시작 중 하나를 진행하는 것이 좋습니다.
참고 항목
- Visual Studio 추가 기능을 검색하세요.
- visualstudio.microsoft.com을 방문하세요.
- Visual Studio 블로그를 참고하세요.
'IT' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Xamarin Mobile Platform 이해 (출처 - 마이크로소프트) (0) | 2019.08.23 |
|---|---|
| 리치리치 사전예약 (0) | 2019.08.22 |
| Welcome to the Visual Studio IDE by MicroSoft (0) | 2019.08.21 |
| 2019년 스마트공장 구축기업 청년체험단사업 참여기업ㆍ참여자 모집 공고 (0) | 2019.08.20 |
| 풍신 1주년 기념 사전예약 (0) | 2019.08.19 |